
Procure-to-Pay (P2P) is the end-to-end flow from purchase requisition through vendor payment, and in India the process must also satisfy Goods and Services Tax (GST) controls such as e‑invoicing, e‑way bills, and Input Tax Credit (ITC) reconciliation to remain compliant and cash‑efficient.
Why P2P matters now
- Indian enterprises operate with multiple ERPs and plants, hybrid documentation like purchase order (PO), goods receipt note (GRN), service entry sheet (SES), gate entry, and challans, which increases handoffs and risk without automation.
- Compliance intensity has risen with e‑invoicing on the Invoice Registration Portal (IRP), IRN/QR checks, e‑way bill ties to movement of goods, and shifting thresholds and timelines that expand coverage to more taxpayers.
- Finance leaders target lower cost per invoice, faster approvals, touchless throughput, and stronger audit trails to capture discounts and protect ITC.
Core problems to fix
- Manual frictions: duplicate invoices, GR/IR mismatches, missing POs, email approvals, and low PO coverage depress first‑pass match rates and slow the close.
- Compliance complexity: field‑level GST and ITC checks require IRN/QR validation, HSN/SAC accuracy, place‑of‑supply logic, and Reverse Charge Mechanism (RCM) handling.
- Data fragmentation: inconsistent vendor masters and plant‑level silos limit real‑time spend visibility and weaken controls.
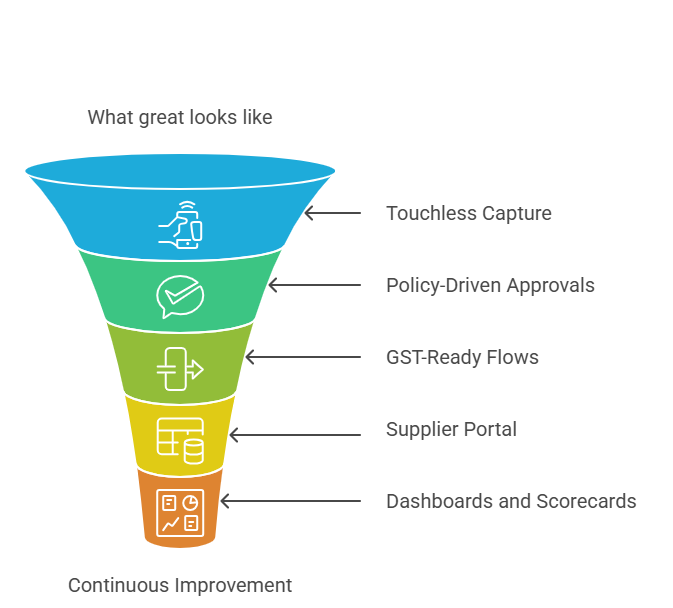
What great looks like
- Touchless capture and validation: AI/OCR powered intake with dynamic 2/3/4/5‑way matching across PO, GRN, quality control (QC), gate entry, and challan reduces human touches and exceptions.
- Policy‑driven approvals: Delegation of Authority (DoA) with mobile approvals, escalation timers, and tamper‑proof audit trails speeds decisions while preserving traceability.
- GST‑ready flows: automatic IRP validation for IRN/QR, e‑way bill triggers from IRN data, tax code determination, place‑of‑supply rules, RCM, and ITC eligibility flags to minimize penalties.
- Supplier portal: onboarding, PO‑flip, e‑invoice upload, dispute collaboration, and status tracking to reduce email loops and cycle time.
- Dashboards and scorecards: cycle time, touchless rate, exception hotspots, discount capture, and compliance KPIs for continuous improvement.
India compliance snapshot
- E‑invoicing is mandatory for businesses above the notified Annual Aggregate Turnover (AATO) thresholds, with IRN/QR authentication and increasing emphasis on 30‑day reporting timelines for larger taxpayers.
- E‑way bill generation can leverage IRN to prefill data, linking logistics movement with the tax invoice to curb evasion and streamline checks.
- ITC reconciliation relies on GSTR‑2B as the static monthly statement for eligibility, replacing prior 2A dependency in annual returns, which tightens documentation discipline.
P2P steps at a glance
- Requisitioning and sourcing: standardized purchase requisitions, catalog buys, and contract linkages reduce maverick spend and speed approvals.
- PO creation and vendor governance: budget checks, approved supplier lists, and vendor master hygiene improve match rates and auditability.
- Goods receipt and inspections: GRN and QC tracking with gate entry and challan integration provide multi‑evidence for 3/4/5‑way match in manufacturing.
- Invoice intake: email, portal, and EDI capture with classification and data extraction sets up touchless matching and tax checks.
- Matching and exceptions: price, quantity, tax, freight, and unit of measure (UOM) validations drive first‑pass throughput, with routed exception playbooks.
- Approvals and compliance: DoA routing with embedded GST checks and IRN/QR verification reduces rework and penalties.
- Payment and reconciliation: on‑time, within‑terms payments with duplicate detection and ledger reconciliation reduce leakage and improve supplier experience.
Mini‑checklist:
- Map and validate GST elements: GSTIN, place of supply, HSN/SAC, RCM flag, and e‑invoice applicability at invoice intake.
- Automate IRN/QR verification and e‑way bill triggers using IRN to prefill EWB data where eligible.
- Build ITC safeguards: vendor compliance status, invoice timeline adherence, 2B reconciliation alerts, and dispute workflows before claiming credit.
- Enable 3/4/5‑way match for manufacturing flows spanning PO, GRN, QC, gate entry, and challan.
- Standardize DoA and exportable, time‑stamped audit packs for statutory and internal audits.
Metrics and maturity signals
- Track cost per invoice, receipt‑to‑approval cycle time, first‑pass match rate, touchless rate, exception and duplicate rates, discount capture, within‑terms payments, and audit findings for a balanced score.
- Maturity indicators include rising touchless rate, falling manual touches and exceptions, and stable within‑terms payments across peak seasons.
Numeric ROI example
- ROI formula: ROI = ((Annual savings − Annualized costs) ÷ Annualized costs) × 100, combining labor time reduction, error/penalty avoidance, discount uplift, improved ITC, and lower rework against license, implementation, change, and support costs.
- Example: Current 60,000 invoices/year at ₹250 = ₹1.5 crore; post‑automation at ₹120 = ₹72 lakh; processing savings ₹78 lakh plus ₹12 lakh discount uplift = ₹90 lakh total savings; annualized platform cost ₹36 lakh; ROI = ((90 − 36) ÷ 36) × 100 = 150%.
Implementation roadmap
- Phase 1: Discovery and compliance mapping (GST, e‑invoicing, e‑way bill), data readiness, and vendor/PO master governance to stabilize inputs.
- Phase 2: Invoice capture and matching automation, DoA approvals, and exception playbooks to move the needle on touchless rates.
- Phase 3: Supplier portal rollout, early‑payment and dynamic discounting programs, and analytics dashboards for visibility and value.
- Phase 4: Continuous improvement—tune rules, expand non‑PO invoices, add advanced discounting, and iterate KPIs quarterly.
Compliance watch‑outs for 2025
- Monitor evolving e‑invoicing thresholds and any reporting timelines such as 30‑day IRN upload requirements for higher AATO bands, and prepare for MFA and other portal controls that affect workflows.
- Align reconciliation cadence to GSTR‑2B timelines to avoid ITC disputes and monthly surprises in cash flow.
Read our next blog – Click here

